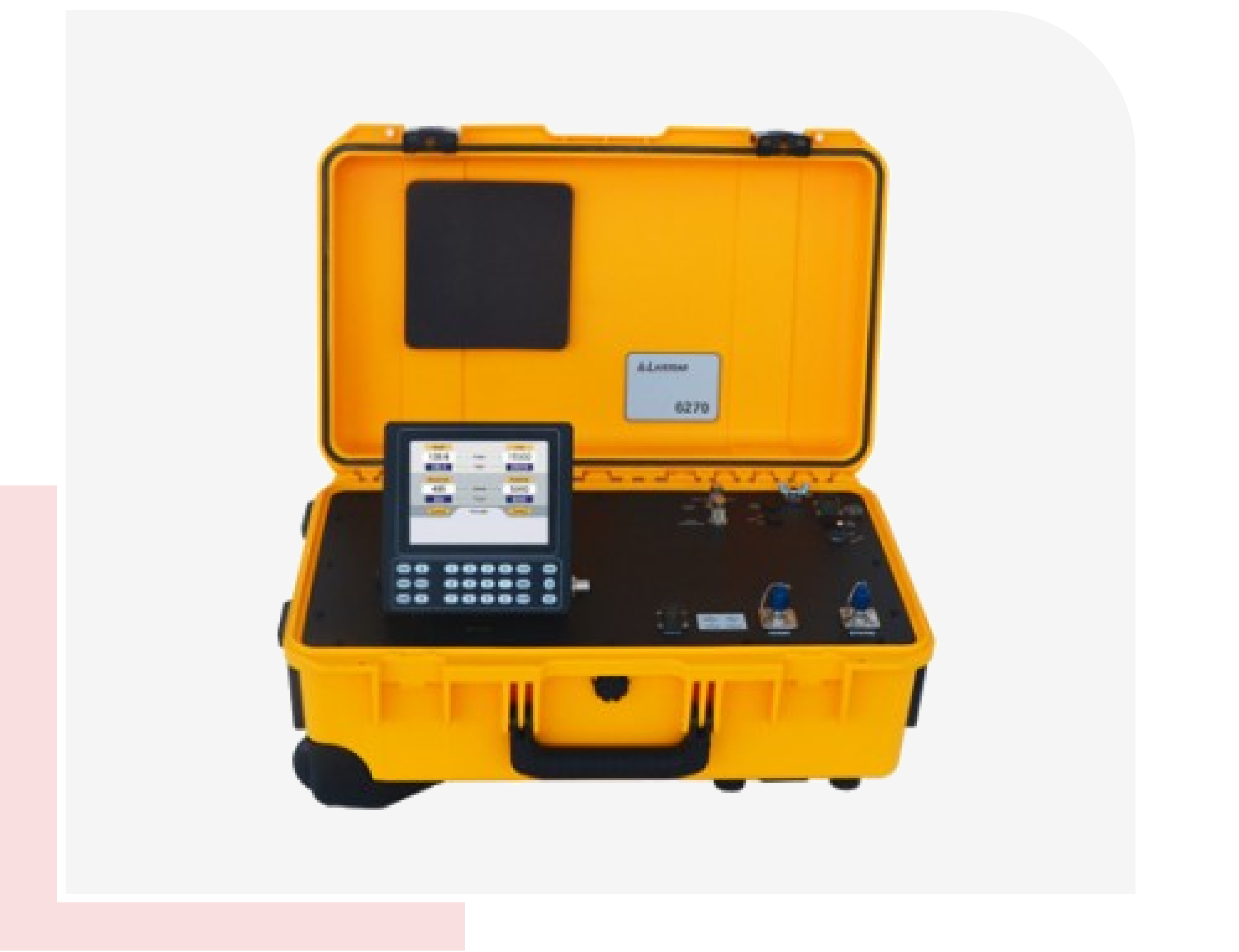
Pitot-Static Checks
The aviation pitot-static system is a critical component in aircraft, providing essential information for safe flight. Let’s delve into how it works and the testing procedures:
Pitot Tube:
-
- The pitot tube is mounted on the aircraft’s exterior, typically on the wing or fuselage.
- It faces into the relative wind (the direction of oncoming air).
- The tube has a small opening that allows impact air pressure (also known as ram air pressure) to enter.
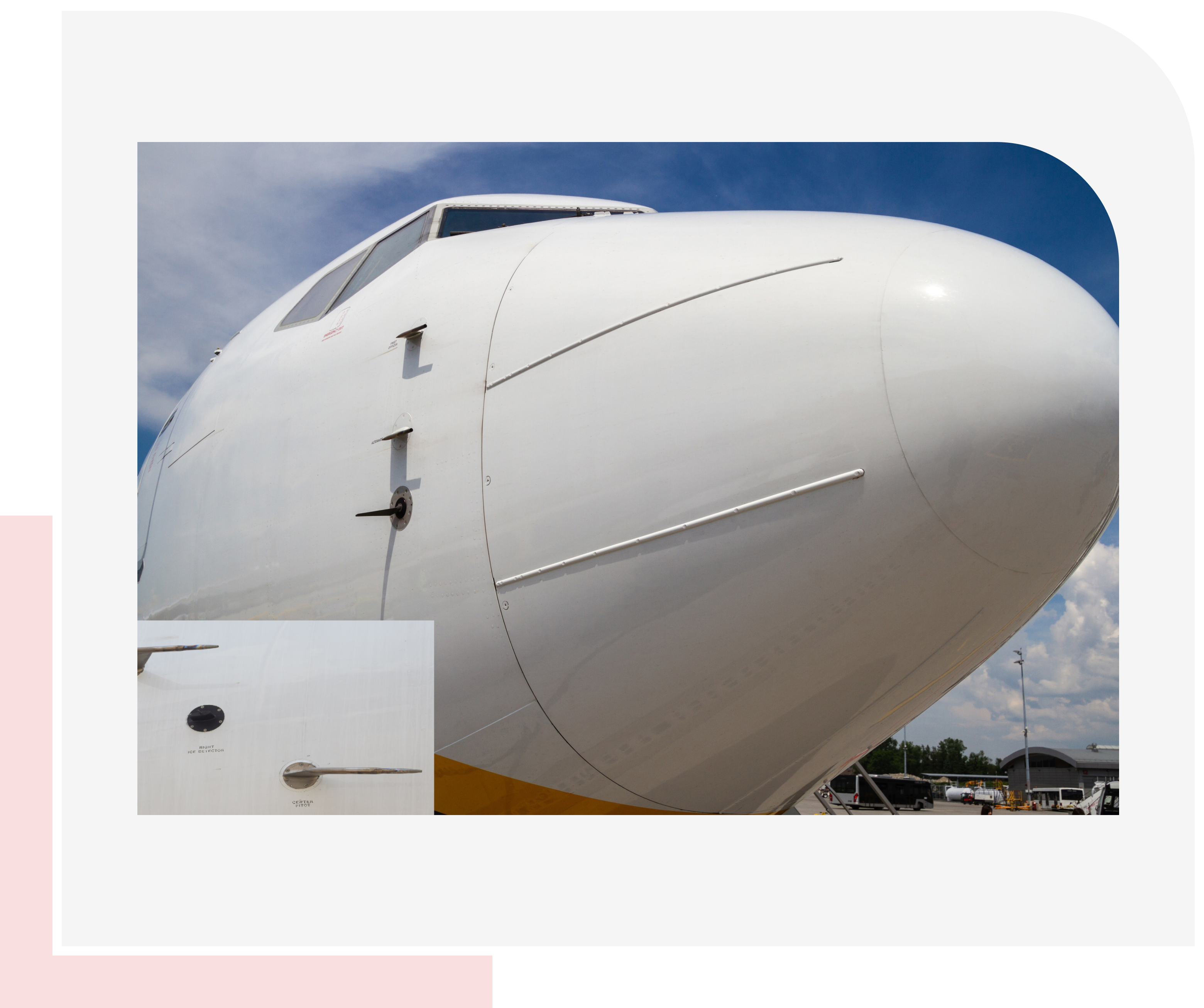


Static Ports:
-
-
- The static ports are attached to the aircraft’s fuselage.
- These ports capture static air pressure, which remains relatively constant regardless of the aircraft’s motion.
- Static ports are usually located away from areas with airflow disturbances (such as near the wingtips).
-
Pressure Differential:
-
- As the aircraft moves through the air, the pitot tube captures the dynamic pressure caused by oncoming air.
- This dynamic pressure increases with the aircraft’s speed.
- The static ports provide a reference for ambient static pressure.

Calculating Airspeed:
-
-
- The difference between dynamic pressure (from the pitot tube) and static pressure (from the static ports) is the pitot-static pressure differential.
- This differential pressure is used to calculate the aircraft’s airspeed.
- The airspeed indicator in the cockpit displays this calculated value.
-
Calculating Altitude:
-
-
-
- The static pressure from the static ports determines the aircraft’s altitude.
- The altimeter measures the difference between ambient static pressure and a standard pressure at sea level.
- As the aircraft climbs or descends, the altimeter adjusts accordingly.
-
-
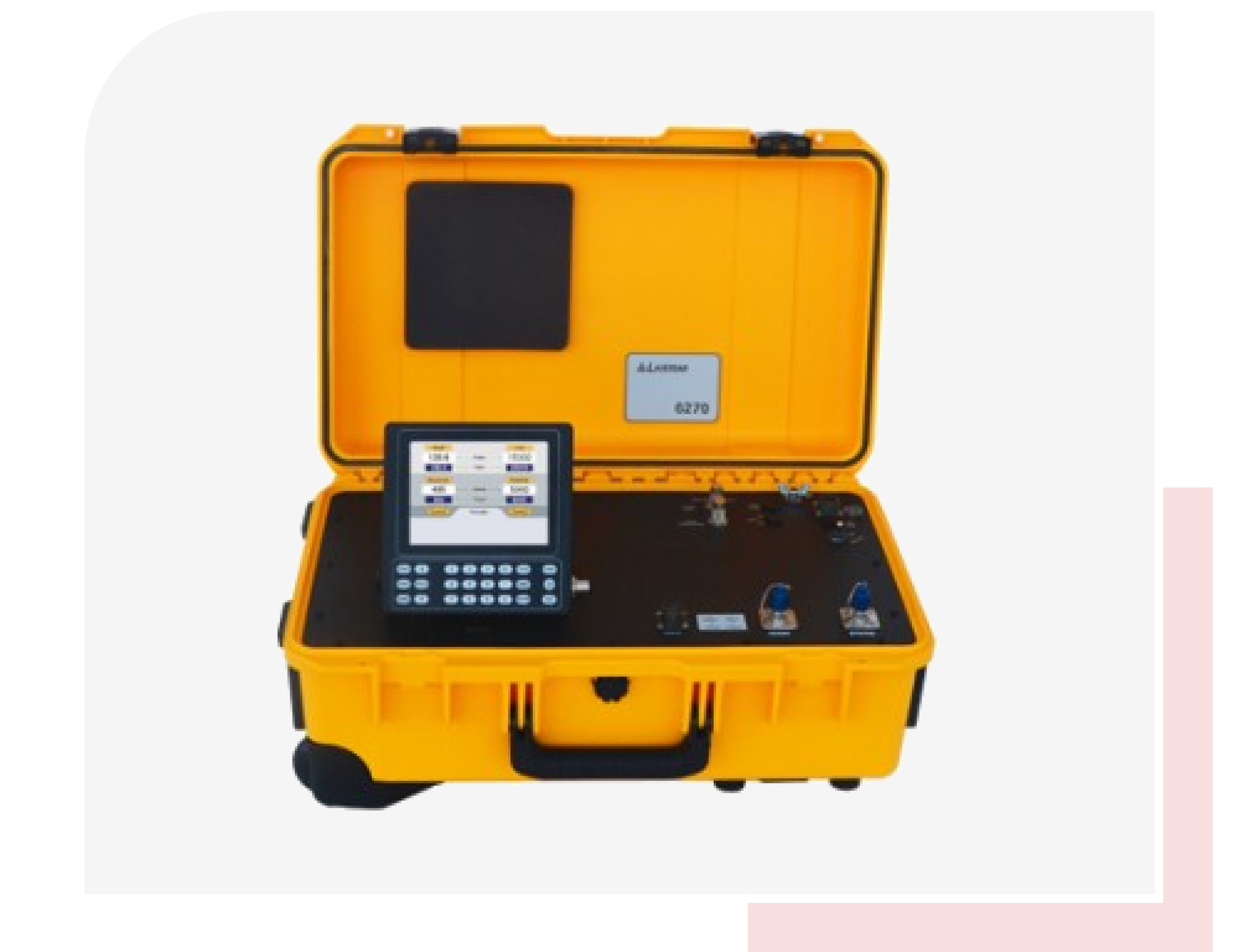


Pre-Flight Inspection:
-
-
- Visually inspect the pitot tube and static ports for blockages, damage or debris.
- Ensure Secure connections and fittings.
-
Leak Testing:
-
-
- Confirm that the pitot and static system are leak-free.
- Pressurize the pitot system and create a vacuum in that static system. This can be done with Laversab Pitot-Static test system and adapters.
-
Static System Test:
-
-
- Connect a Pitot-Static test system through aircraft adapters to the static port.
- Simulate various altitudes to test the system’s accuracy.
-
Pitot-Tube Test:
-
-
- Connect a pitot-static tester to the pitot tubes through aircraft adapters. Depending on the aircraft, there may more that one pitot tube.
- Use the pitot-static tester to create a pressure differential between the ram pressure and static pressure. This will simulate airspeed.
- Blockages due to FOD, insects, or ice can affect accuracy.
- Consult the aircraft’s manual for error correction.
-





